What did scientists discover?
Human hemoglobin is a protein responsible for oxygen transport in the blood. It consists of two "alpha" and two "beta" subunits. Researchers have identified more than 1,500 structurally abnormal hemoglobins in human patients, some of which cause debilitating diseases, including sickle cell disease, which afflicts millions of people throughout the world.
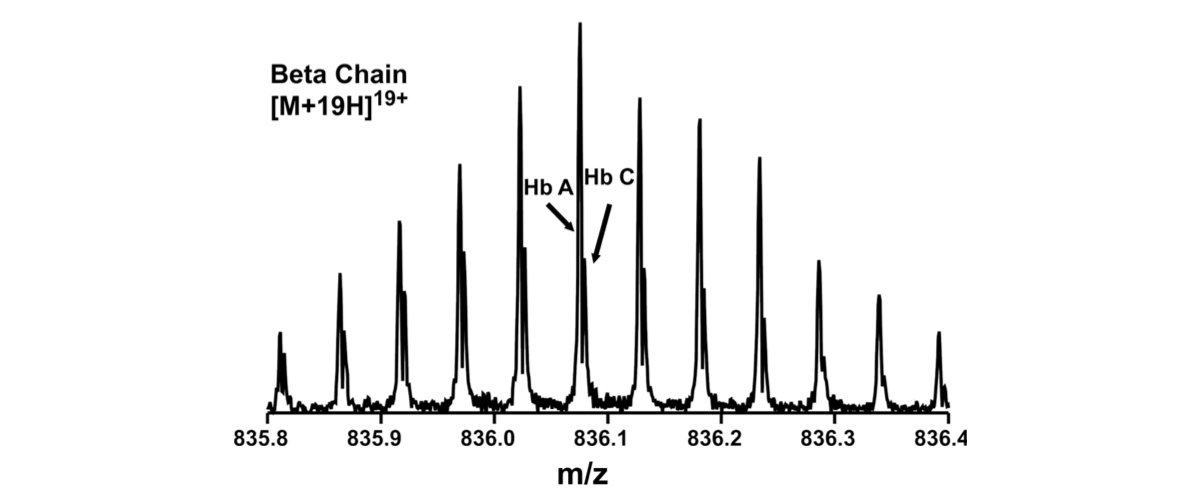
There is currently no rapid way to confidently identify unknown hemoglobin variants. However, a collaboration of MagLab users recently reported a comprehensive, fast, and accurate characterization of hemoglobin for clinical diagnosis of human blood by using the unique capabilities of the MagLab's 21T Fourier Transform ‒ Ion Cyclotron Resonance (FT ‒ ICR) mass spectrometer.
Why is this important?
The method has successfully identified variants in hemoglobin in a few minutes, including a newly-discovered variant, thereby holding promise to provide clinicians with a valuable new tool for personalized medicine.
Who did the research?
L. He1, A. L. Rockwood2,3, A. M. Agarwal3,4, L. C. Anderson5, C. R. Weisbrod5, C. L. Hendrickson1,5, A. G. Marshall1,5
1Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Florida State University; 2Rockwood Scientific Consulting; 3University of Utah Health; 4ARUP Institute for Clinical and Experimental Pathology; 5Ion Cyclotron Resonance Program, National MagLab
Why did they need the MagLab?
This analysis requires ultrahigh mass resolving power and mass accuracy to confidently identify the hemoglobin amino acid sequences, a feat which is best accomplished by the MagLab's 21 tesla FT ‒ ICR mass spectrometer.
Details for scientists
- View or download the expert-level Science Highlight, Identification of Abnormal Hemoglobin from Human Blood
- Read the full-length publication, Diagnosis of Hemoglobinopathy and β-Thalassemia by 21-Tesla Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Hemoglobin from Blood, in Clinical Chemistry
Funding
This research was funded by the following grants: G.S. Boebinger (NSF DMR-1157490, NSF DMR-1644779)
For more information, contact Chris Hendrickson.